SYNTHETIC EXOSOMES
WHAT ARE EXOSOMES?
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles of natural origin that are produced by all cell types in the range of 40 to 160 nm. They have a key role in cell-to-cell communication and have been proved to be powerful tools in diagnosis and therapeutics.
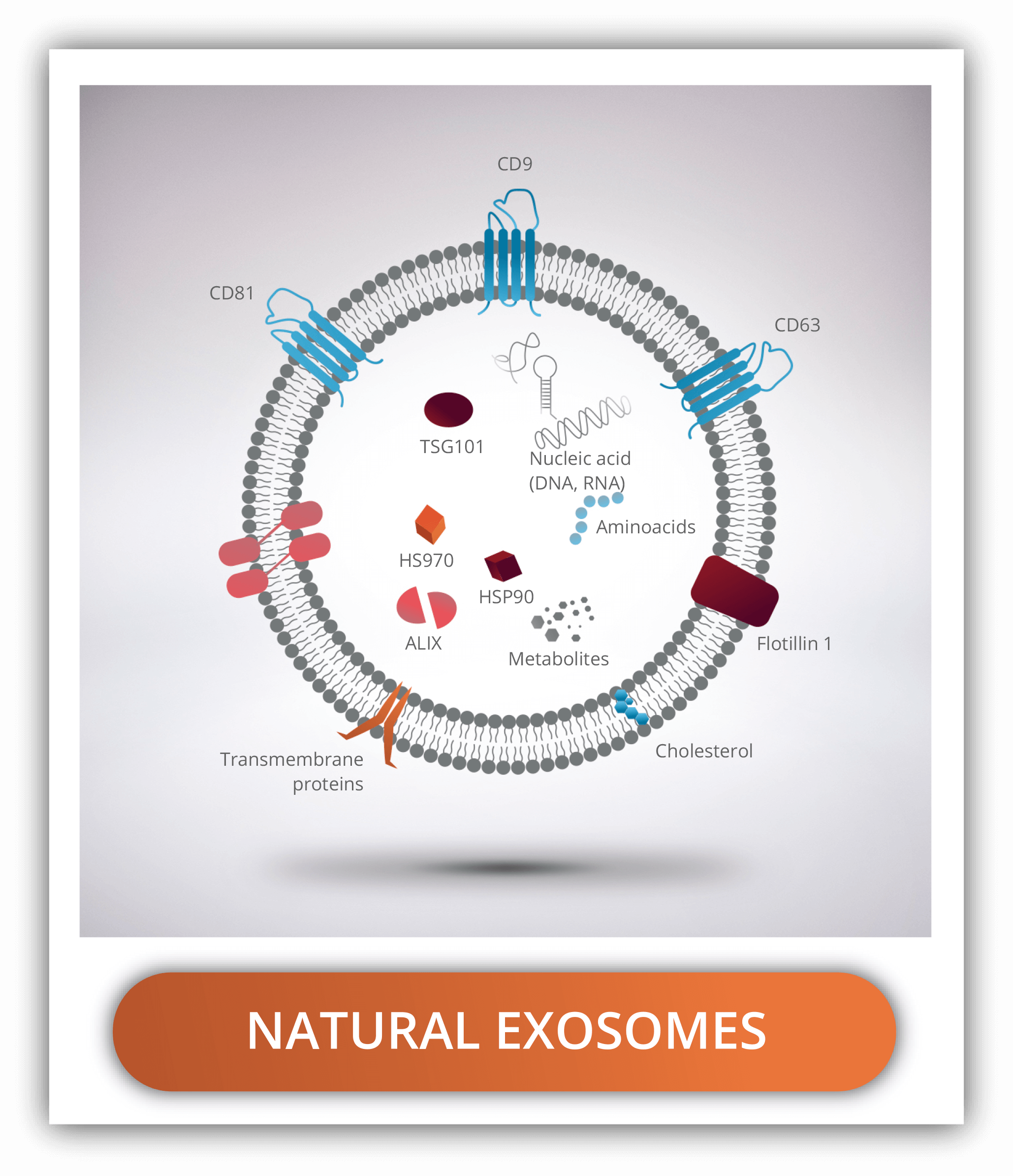
Their basic structure is very similar to liposomes, consisting of double lipid which is a slice of cell membrane and an aqueous based core which will be a part of cell plasma. For this reason, exosomes are rich in biological molecules, containing transmembrane proteins and receptors in their surface, as well as comprising nucleic acids, amino acids, metabolites, and other molecules within.
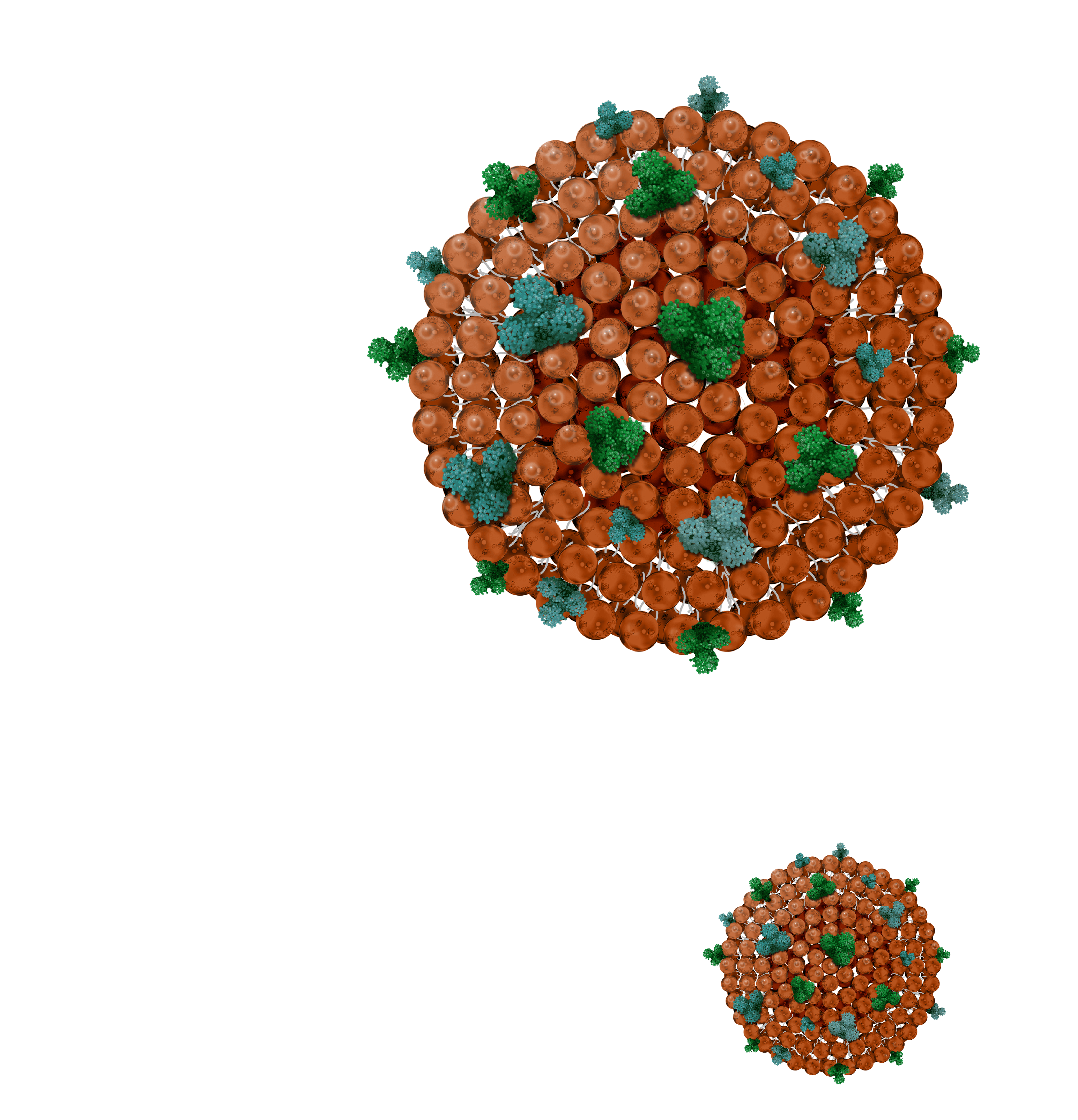
Exosomes then, act as delivery agents, for different biological purposes:
- Genetic expression regulation
- Survival and proliferation signalling
- Angiogenesis and wound healing stimulation
- Waste management
- Immunity triggering and balance
- Receptor ligand specific signalling
- Apoptosis control
- Cellular differentiation
- Indication of cellular migration and metastasis
- Metabolic programming
As mentioned above, exosomes are produced by all types of cells, and are formed by the endogenic pathway. The cell membrane folds inward, in a process called invagination, forming a lipid vesicle: the endosome. Then, inside the cell, macromolecules as proteins and genetic material are incorporated into the endosome, again by invagination, creating multiple exosomes. Finally, the endosome membrane fuses with the cell membrane to release these vesicles to be received by other cells.
Natural exosomes are very difficult to obtain and require expensive and strict purification and analytical procedures. For this reason, multiple technologies have been developed to synthesize extracellular vesicles very similar to exosomes.
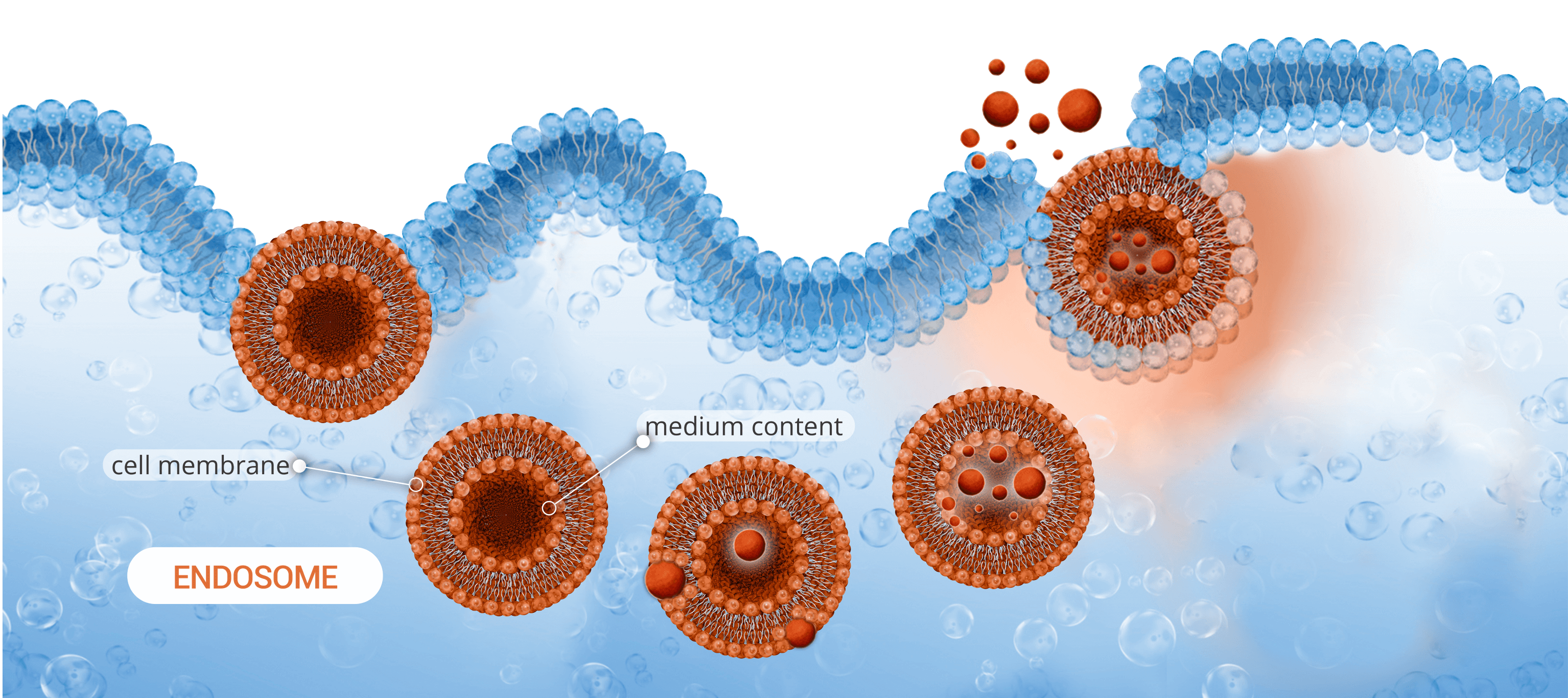
WHAT ARE SYNTHETIC EXOSOME DELIVERY SYSTEMS?
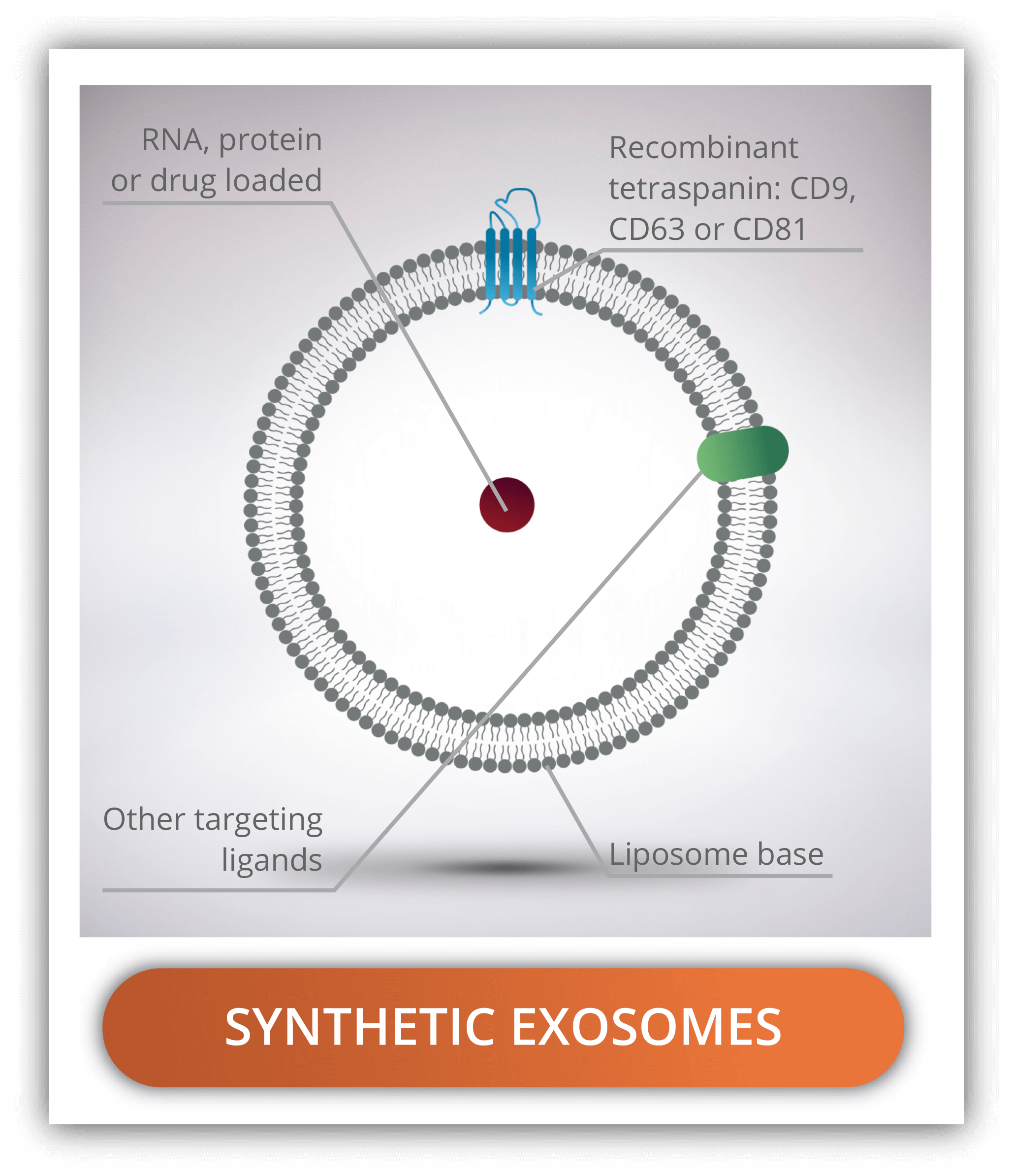
Synthetic exosomes are outstanding drug carriers since they resemble cellular communication mechanisms. However, unlike natural exosomes, size and composition can be easily controlled and scalable for its use in preclinical or clinical settings. Since the assembly process can be monitored, it results in the formation of “clean”, well-characterized drug delivery systems. To date, exosomes have been used in many studies for tissue regeneration, delivery of drugs and genes, and diagnosis of diseases.
EXOSOME PROPERTIES AND CLASSIFICATION
Although exosomes are greatly heterogeneous, they can be classified according to the following criteria:
Size
There are three main groups of exosomes according their size: Exo A: 40-75 nm, Exo B: 75-100 nm and Exo C: 100-160 nm.
Biomarker
There are three transmembrane proteins used to identify exosomes: CD63, CD9 and CD81
Cell function
Exosomes as was stated earlier, serve many purposes, and can be classified as pro-survival, pro-apoptotic and immunomodulating.
Source
All cell types produce exosomes, so their source is also a classification tool: brain-derived exosomes, liver-derived exosomes and pancreas-derived exosomes are three examples.
NATURAL VS ENGINEERED VS SYNTHETIC EXOSOMES
Natural exosomes produced endogenously by cells present some limitations such as homogeneity, expensive and difficult isolation as well as poor targeting specificity. For application in the clinical field, loading of exosomes with pharmaceuticals and targeting are required. For those reasons, several alternatives have been developed. Mainly, those being hybrid and synthetic exosomes.
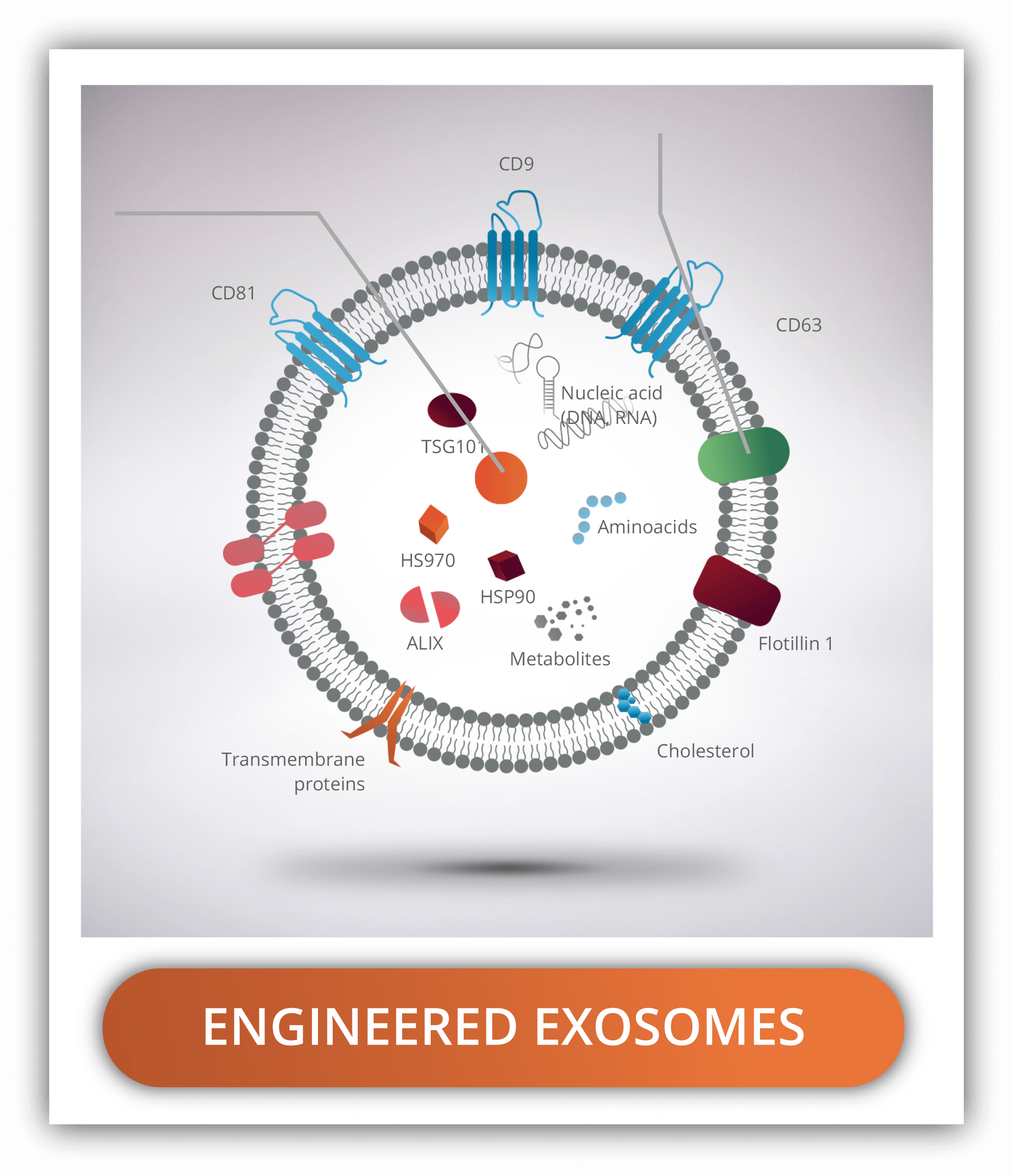
ENGINEERED EXOSOMES
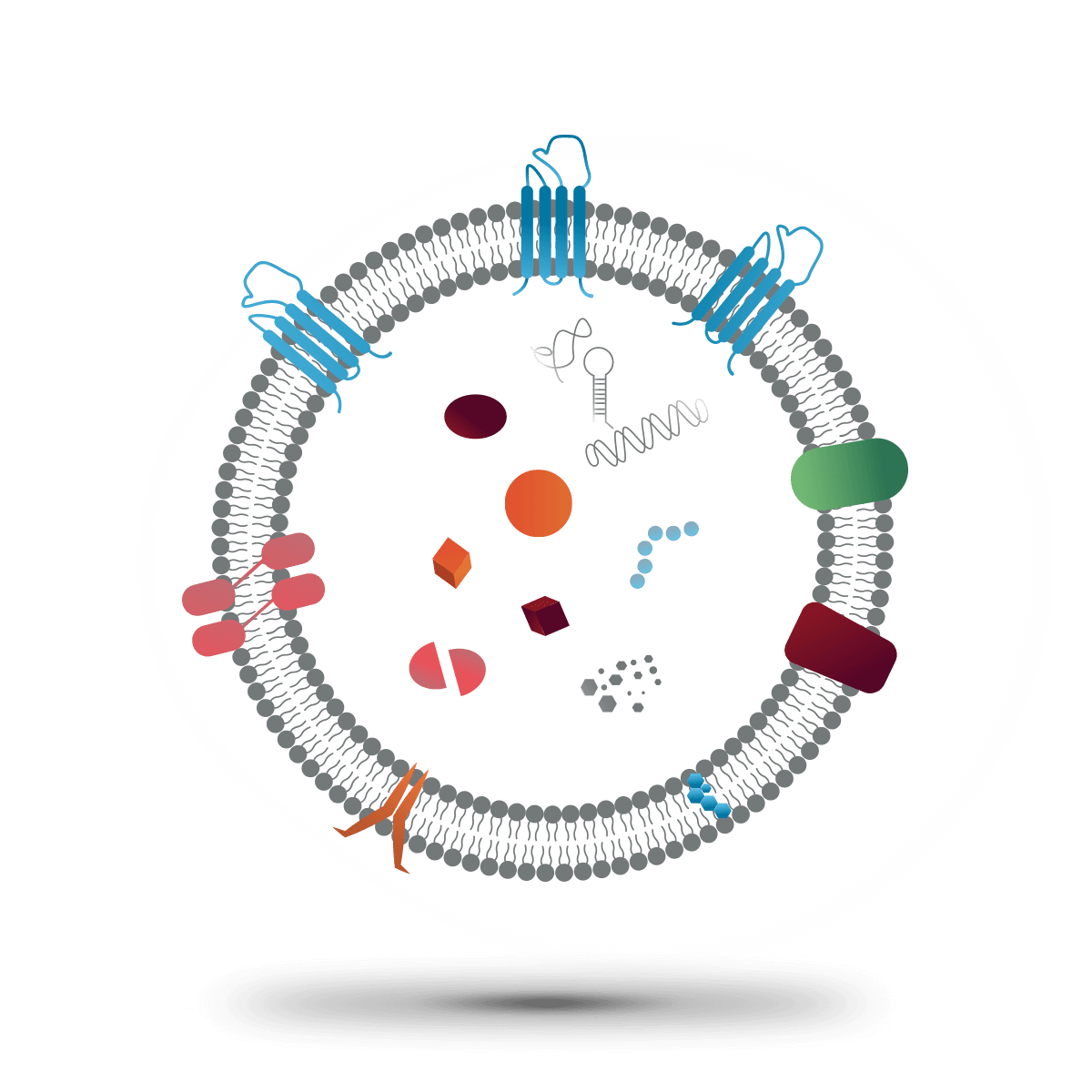
Alteration of natural exosomes has been labelled under the umbrella term of engineered or designer exosomes. The aim of this process is to display targeting molecules or loading therapeutical compounds within. This type of exosomes can be obtained by two different approaches, through parental cell-based engineering or direct post-isolation engineering, from more to less complex.
In the first case, the cells are genetically modified to produce exosomes with the components of interest in vivo. With this approach, labelling or targeting proteins can be placed in the surface or other components delivered inside. An example could be the production of a protein with an exosome signalling peptide (CD63, CD9, CD81, GPI and Lamp2b), that will lead to the embedding in the exosome membrane. If the molecule is desired to be transported within, other tags can be used to direct the MSMs or Molecule Sorting Module system. This MSMs is the responsible for sorting the proteins and RNA that will be directed to the exosome. For example, ubiquitination tags have been proved to help in this process.
The second approach, direct post-isolation engineering, involves the modification of the exosomes after the isolation has been done. The addition of molecules in the exosomes can be achieved by manipulation methods such as sonication extrusion, incubation, freeze-thaw and bioconjugation. Another strategy for post-isolation modification is the fusion with synthetic liposomes containing the desired components, producing what are called hybrid exosomes.
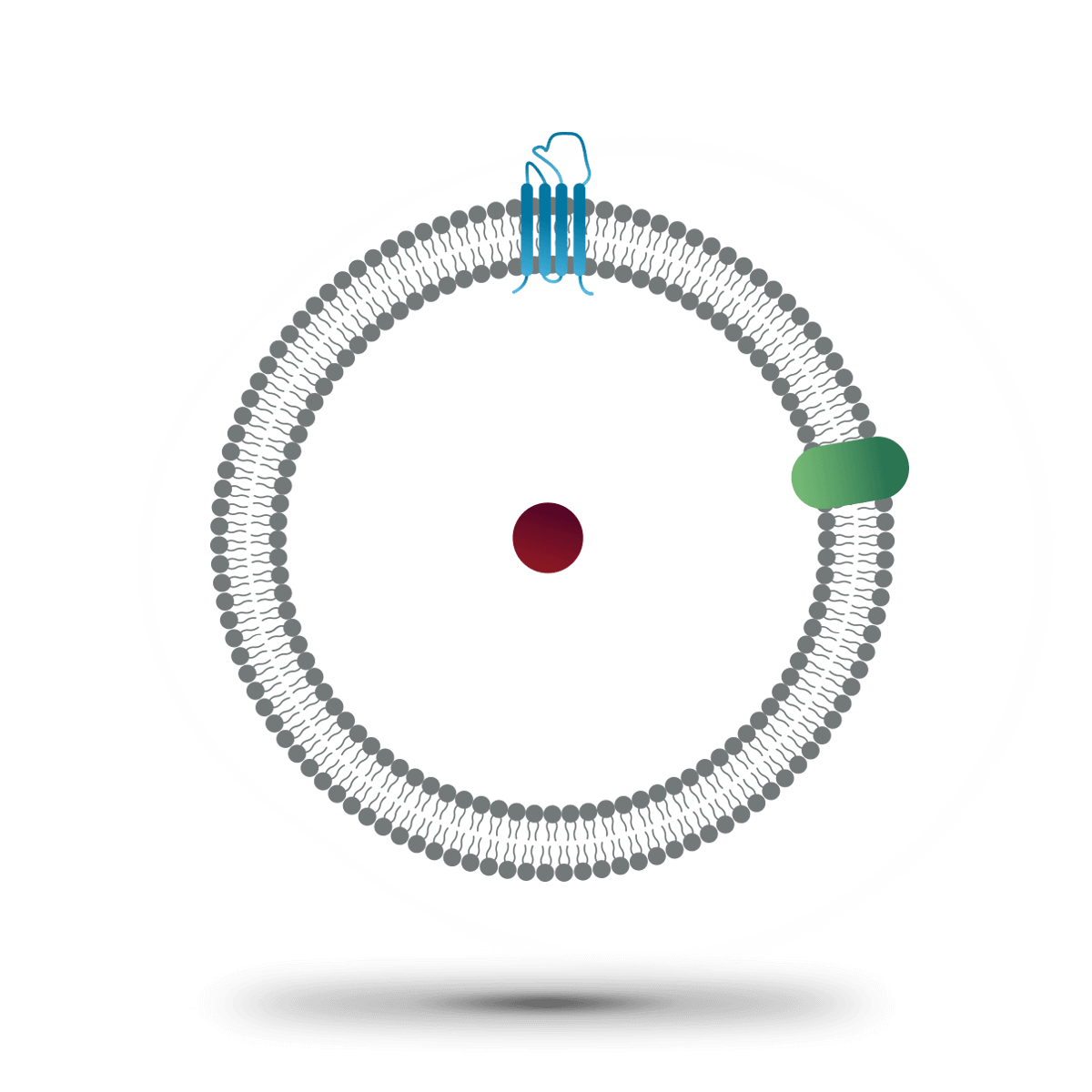
SYNTHETIC EXOSOMES
In the bottom-up strategy we have fully synthetic or artificial exosomes using plain liposomes as a blank canvas and adding the characteristic exosome markers, lipids and contents (proteins and RNA). Also referred to as exosome-mimetics, the synthetic exosomes are less variable and allow the incorporation of targeting ligands and contents in an easier and controlled manner. They are more suitable for pharmaceutical uses since they are highly reproducible and easier to scale up the manufacturing.
USES AND APPLICATIONS
![]()
VALIDATION
& QUALITY CONTROL
![]()
CANCER
TREATMENT
![]()
INMUNOMODULATING RESPONSE
![]()
MOLECULAR
THERAPY
![]()
BRAIN DRUG
DELIVERY
![]()
OCULAR DRUG DELIVERY
![]()
TISSUE
ENGINEERING
WHAT KIND OF DRUGS MAY BE DELIVERED BY SYNTHETIC EXOSOMES?

Proteins and enzymes

Genetic material
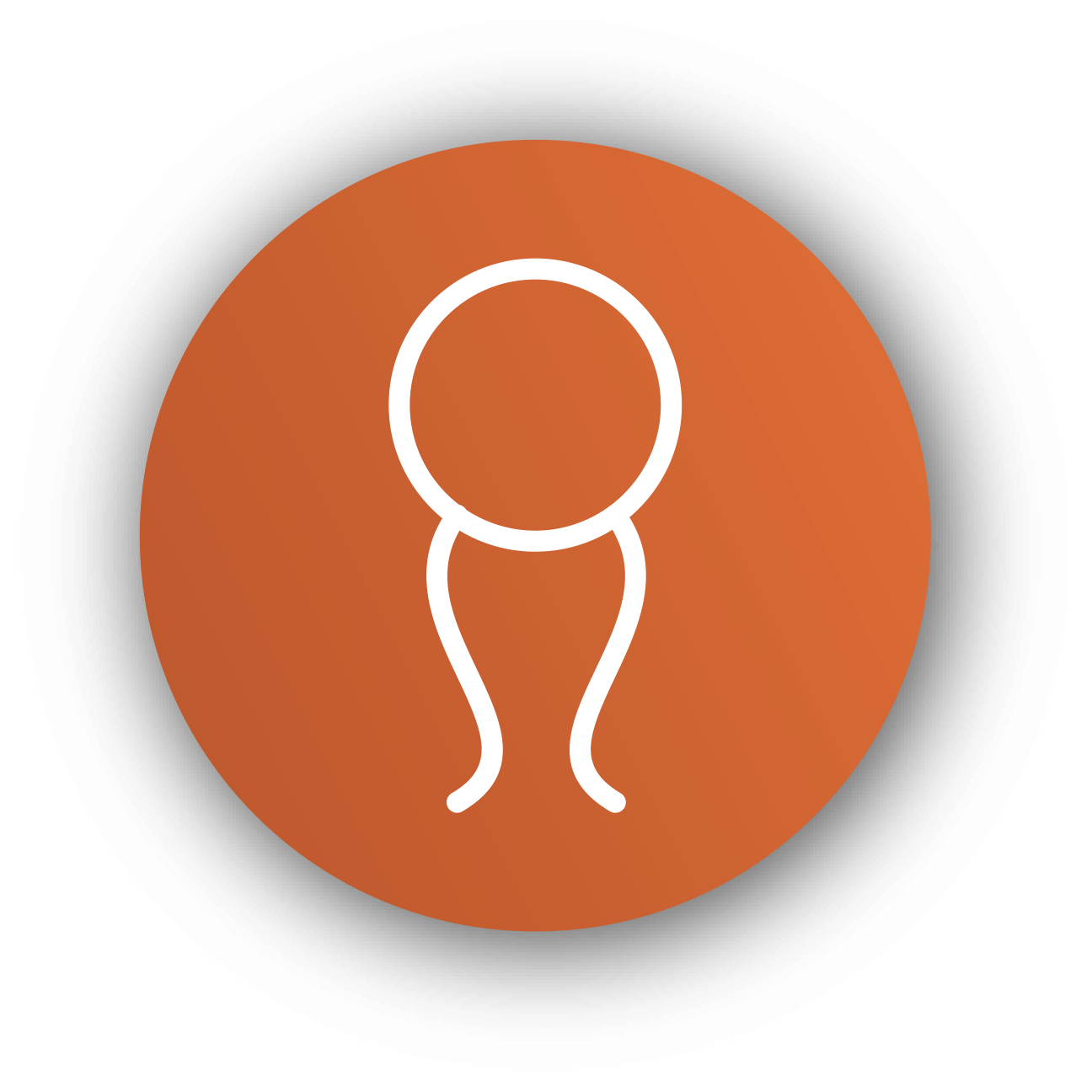

Lipophilic compounds
Pharmaceutical drugs
HOW CAN SYNTHETIC EXOSOMES RESEMBLE NATURAL EXOSOMES?
The heterogeneity of exosomes depends on the cell source and its function. Exosome composition is complex and is not viable to artificially incorporate every protein and RNA present in a cell-secreted exosome. For this reason, it is key to first understand what are the contents that lead to the functionality of the exosome. The most important ones are membrane ligands and RNAs.

Tetraspanins from exosomes
Tetraspanins are transmembrane proteins with four hydrophobic domains inserted in the lipidic membrane. They are key players in the signal transduction field, where they play a part in cell proliferation, adhesion, membrane fusion, immune system activation, protein trafficking and cell migration. CD9, CD81 and CD63 are the main membrane proteins present in natural exosomes, being considered exosome markers. They are indispensable for exosome mimics.
- CD81 tetraspanin: it complexes with integrins, with the immunoglobulin superfamily member 8 and CD36. It has been related to the stimulation of cell proliferation and signal transduction, interacting with membrane proteins of the B cell and T cells, and as such, having immunomodulatory effects.
- CD9 tetraspanin: it interacts with other tetraspanins (CD63) as well as with integrins (α1β1), immunoglobulin SF members (intercellular adhesion molecule 1 or CD54), growth factors (Pro-TGF-α) and immune system molecules (CD4). It has a role in platelet activation and aggregation, and immune response by interaction with neutrophils. Studies show that is also involved in cancer metastasis since it regulates cell adhesion and migration.
- CD63 tetraspanin: It associates with integrins (CD18), TIMP-1 and other viral proteins. As other tetraspanins, it participates in migration, proliferation, and cell signalling.
Other ligands
- Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)
- Platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFRs)
- Lactadherin (C1C2 domain)
- APO2L/TRAIL: For immune regulation, tumoral cells targeting
- MHC peptide complexes: T-cell targeting
- Antibodies: For example, DEC205 monoclonal antibody for specific targeting of dendritic cells to induce immune responses.
- Integrin α6β4: Binds to laminins, for targeted delivery in cancer cells (lung)
- Cx43 proteins: Conexin protein that allows cellular communication, involved in the coordination of muscle contraction and inflammation

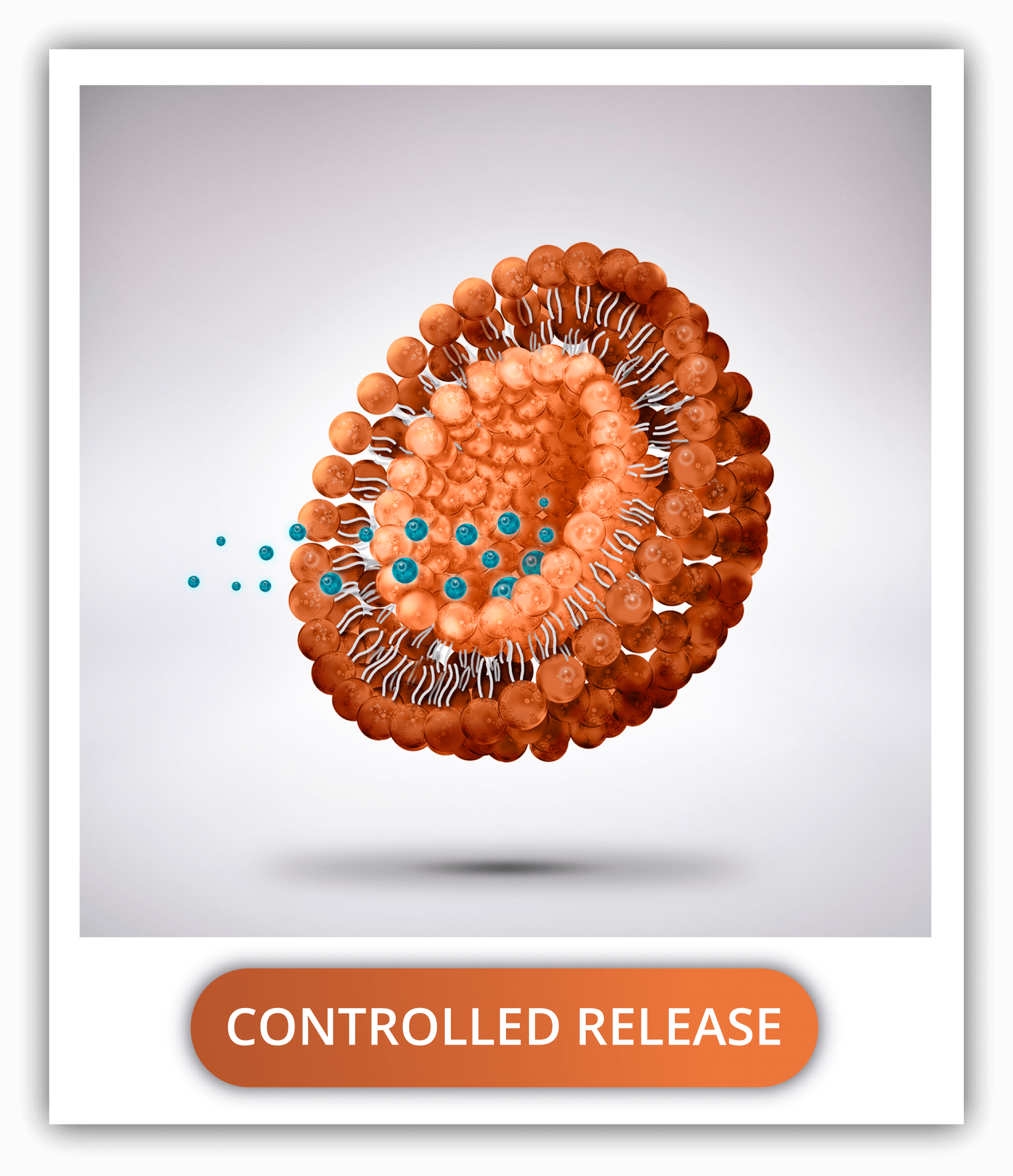
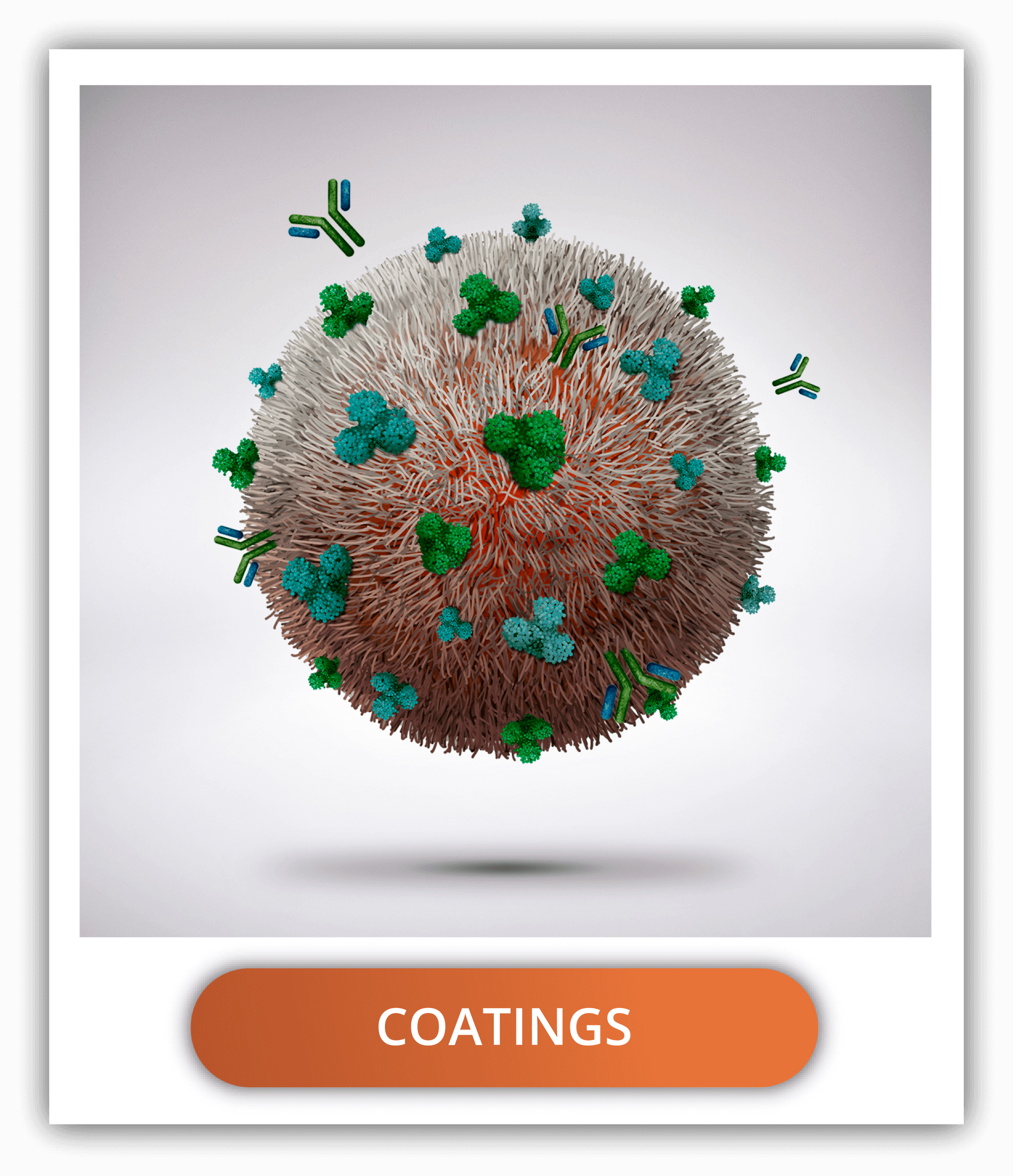
HOW DO SYNTHETIC EXOSOMES PROVIDE A WAY OF TARGETING DRUGS TO A SPECIFIC TISSUE?
Exosome physico-chemical properties must be tailored to every delivery project to yield the expected therapeutical effects.
Regarding exosome composition, there is a wide range of phospholipids with different features that allow the control of its targeting abilities:
- Fluorescence phospholipids for tracking and imaging applications
- Cationic phospholipids for gene delivery
- Anionic phospholipids like phosphatidylserine for immune system targeting
- PEGylated phospholipids for stealth delivery
- Functionalized head groups for the covalence union of the lipid with targeting compounds such as peptides or antibodies
- pH ionizable phospholipids for mRNA delivery
- Addition of coating compounds for targeting like chitosan, PEI, pectin, or hyaluronic acid
The physical properties such as size and lamellarity are closely related to its pharmacokinetics and drug loading capacity. They depend on the composition but mainly on the production methods, and thus, can be adjusted for each target.
Size and lamellarity are directly proportional to the amount of drug it can encapsulate since they increase the volume of the compartments accommodating both hydrophilic (core) and hydrophobic (membrane) compounds.
BUY SYNTHETIC EXOSOMES FOR DRUG DELIVERY
Do you have a drug delivery project compatible with synthetic exosomes? Get in contact with us and tell us a little bit about your project. We will assess you and prepare a synthetic exosome design that ensures your success.
