CHARACTERIZATION
We provide your lab with the most valuable information about your nanomaterials that can help you control the quality of your products. We count with the most advanced equipment and technology to fully analyse all the physical and chemical properties of your interest. Characterization allows the prediction of the behaviour of the nanomaterials like long term stability or in vivo distribution.
PARAMETERS OF INTEREST

 Drug Loading
Drug Loading
 Size and distribution
Size and distribution
 Morphology analysis
Morphology analysis
 Particle surface charge
Particle surface charge
 Particle concentration
Particle concentration
 Entrapment efficiency
Entrapment efficiency
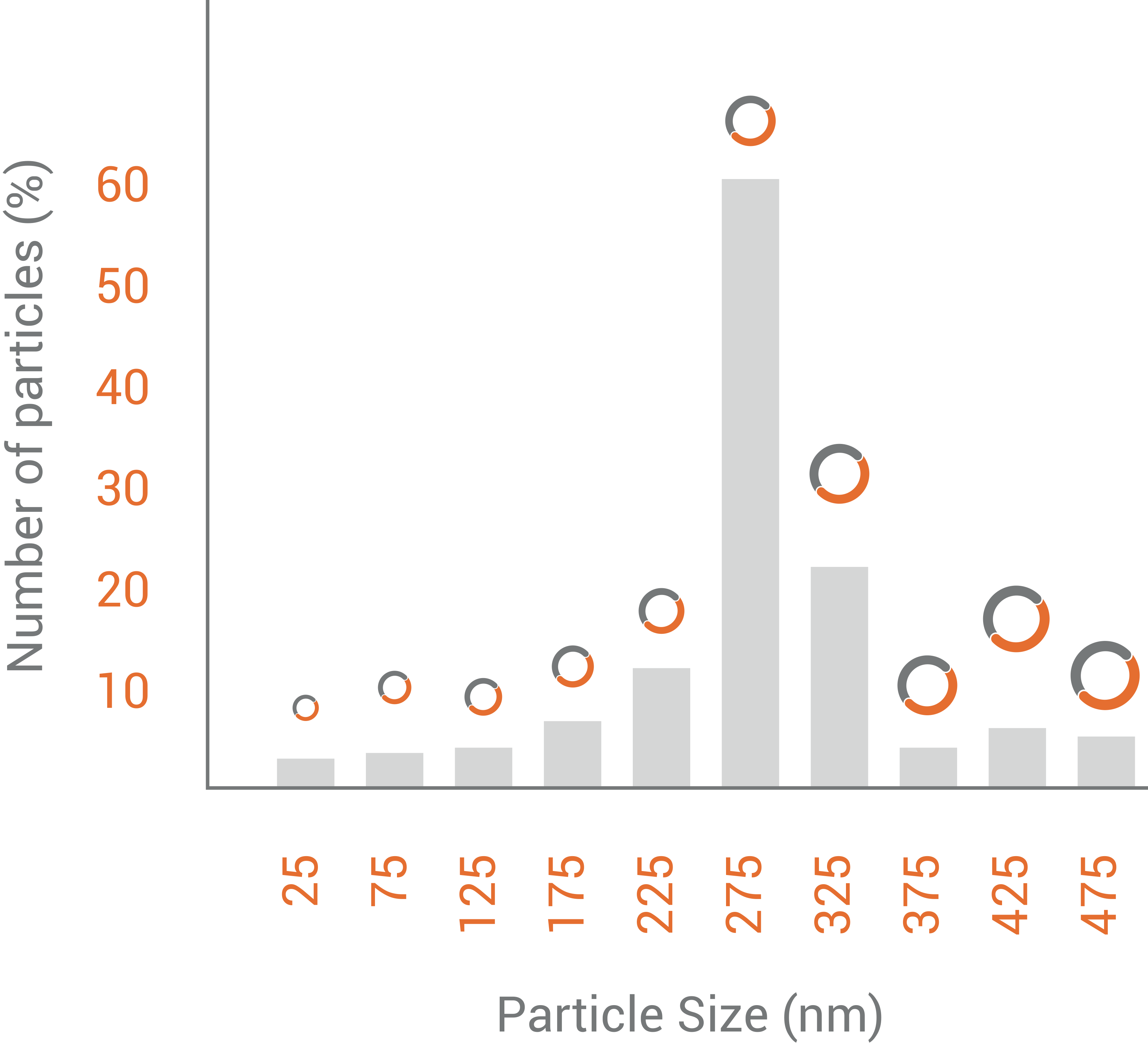
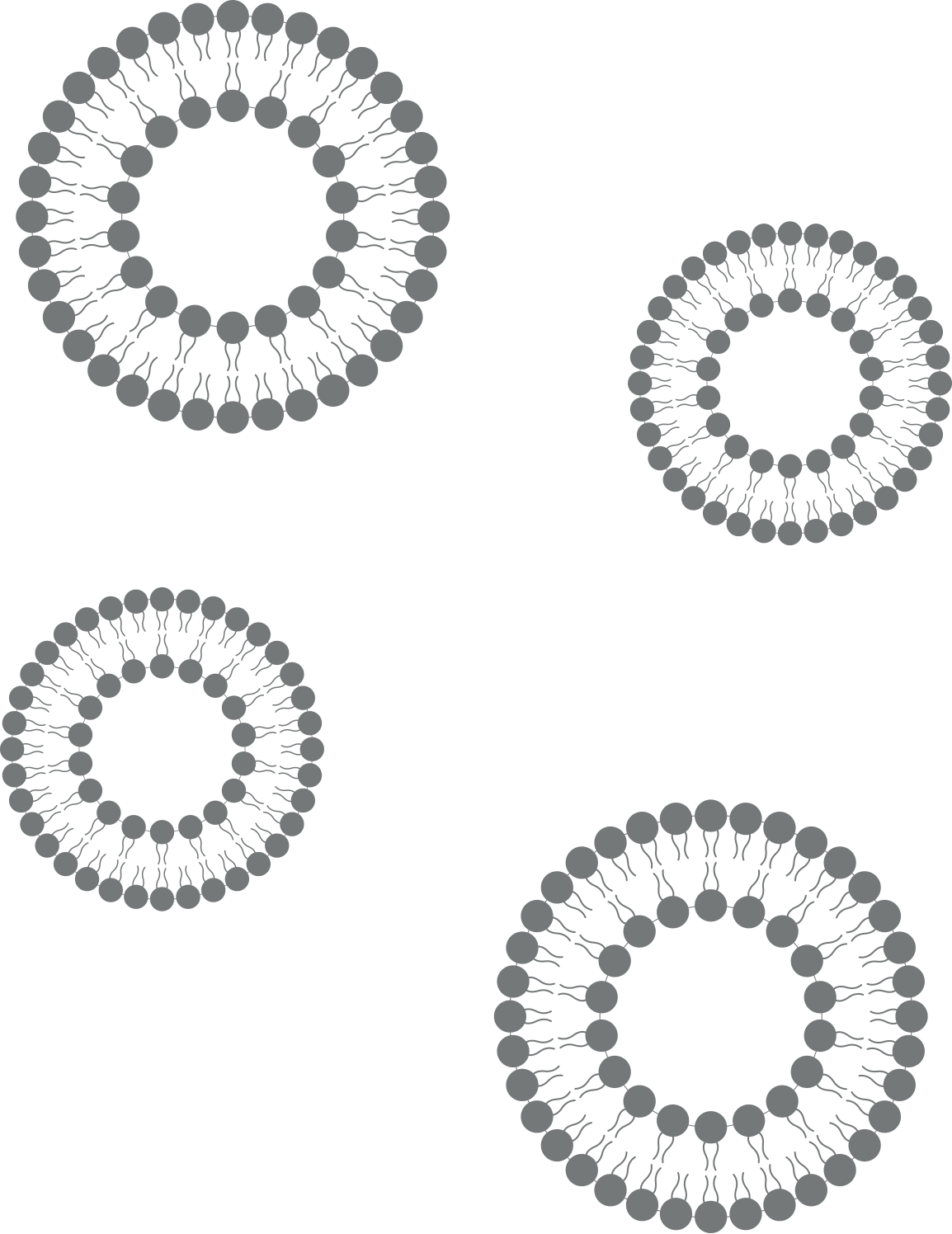
Size and size distribution
Determined using Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) or Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA). The information provided by those techniques is the mean size and size distribution of the particles in suspension, whether they are nanovesicles, polymeric and inorganic nanoparticles, exosomes, or other nanostructures. It is a crucial parameter that influences its performance in in vivo treatments and thus therapeutic effectiveness as a result.
Among other processes it affects:
![]() In vivo distribution
In vivo distribution
![]() Organ and organelle accumulation and uptake
Organ and organelle accumulation and uptake
![]() Renal and liver clearance
Renal and liver clearance
![]() Drug loading capacity
Drug loading capacity
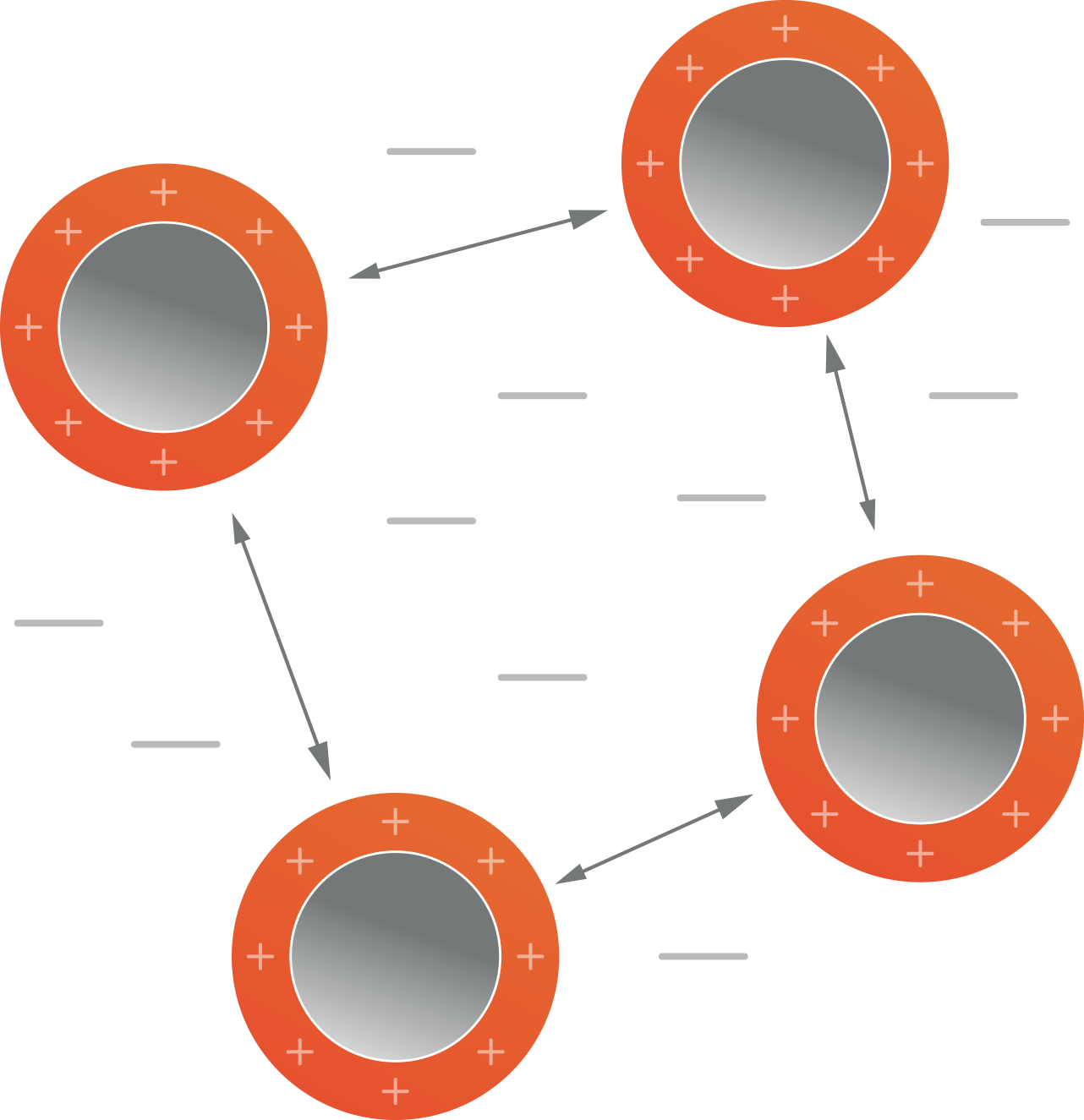
Particle surface charge
Also referred to as Z-potential, is defined as the difference between the charge of the nanoparticle surface and the dispersion it is within. It measures the degree of repulsion between the nanoparticles, and consequently the likelihood of aggregation. It can be used as a:
![]() Predictor of long-term stability
Predictor of long-term stability
![]() Assessment of coating effectiveness
Assessment of coating effectiveness
![]() Indicator of potential cell adhesion
Indicator of potential cell adhesion
Particle concentration
By means of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) particle concentration can be measured in real time. Like the size, particle concentration is an important factor to be considered for the following reasons:
![]() Toxicological problems
Toxicological problems
![]() Drug delivery efficiency
Drug delivery efficiency
![]() Regulatory requirements
Regulatory requirements
![]() In the case of exosomes, it may be linked to disease
In the case of exosomes, it may be linked to disease
Morphology analysis
Proper morphology plays an important role for the correct performance of the nanoparticles. The structural information can be obtained with various techniques like:
![]() Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
![]() High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM)
High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM)
![]() Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
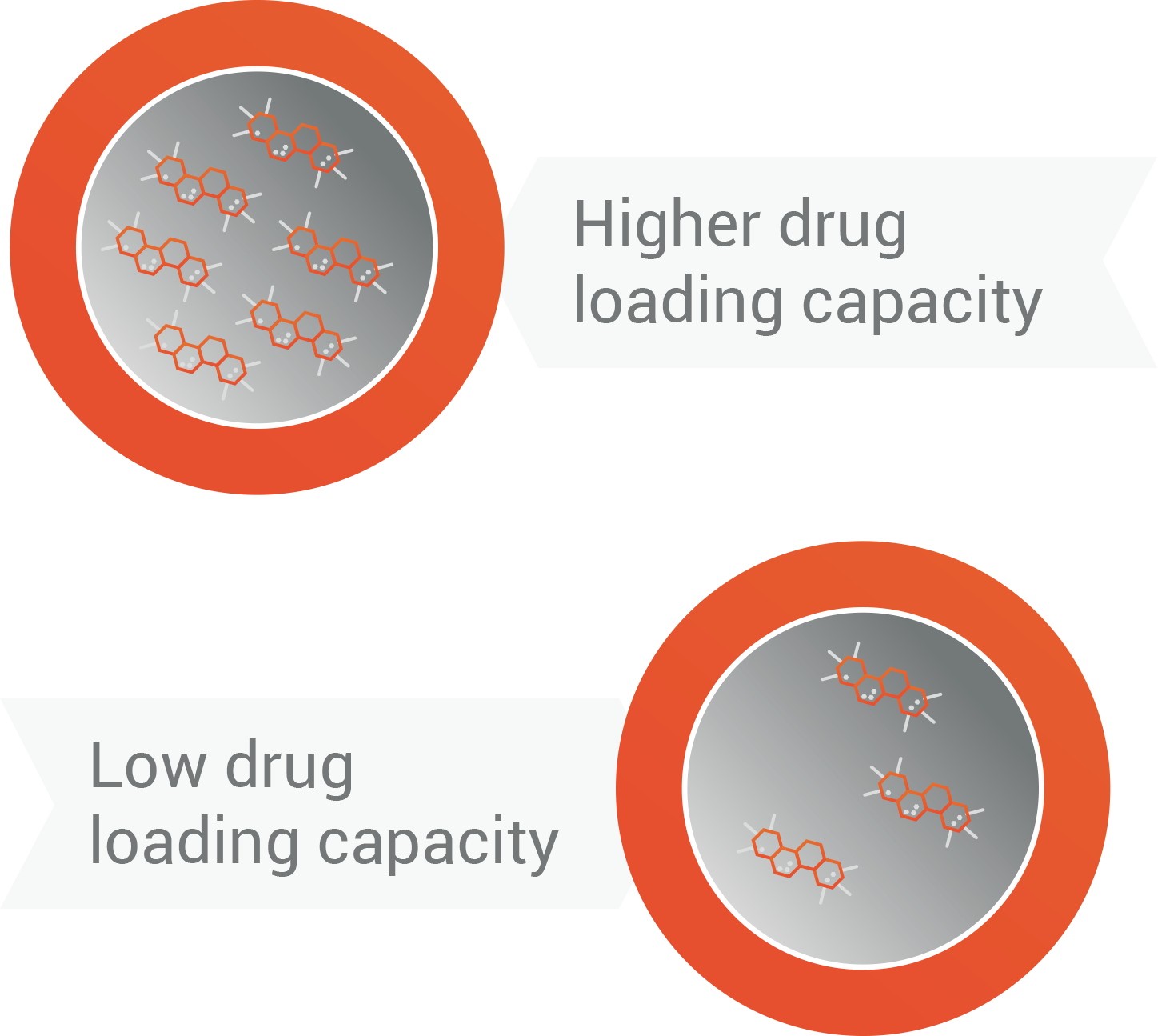
Drug loading capacity
The drug loading capacity is the amount of the active principle that is encapsulated per weight of nanocarrier. Depending on the application and type of active principle, it may need to be adjusted to reduce the toxicity of the drug or modify the speed of delivery.
This can be done by modifying the components ofthe nanoparticle. It can be measured by different techniques as UV-visible spectrophotometry or highperformance liquid chromatography.
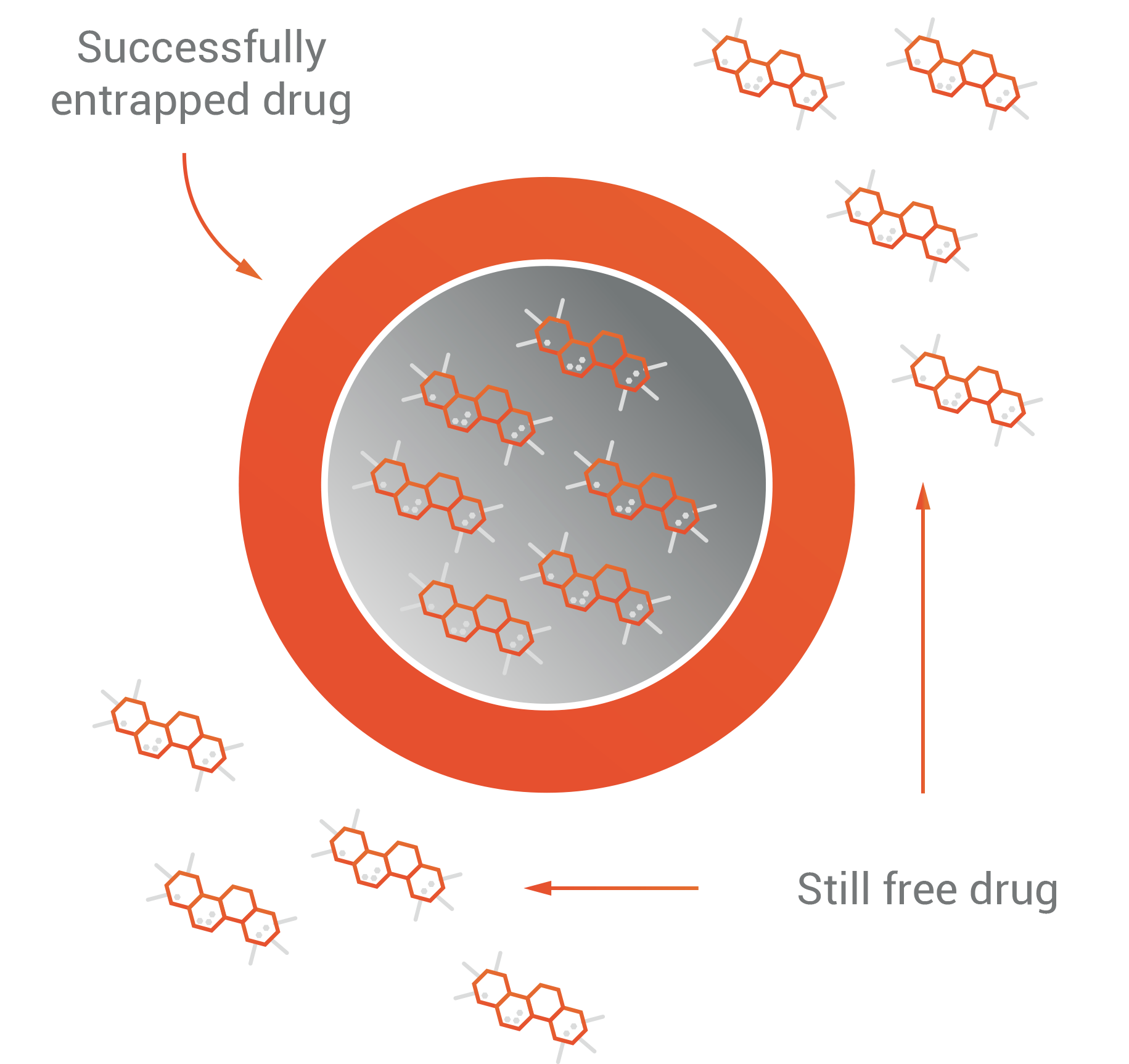
Entrapment efficiency
The entrapment or encapsulation efficiency is the amount of product that has been successfully entrapped by the nanovesicles. The higher the encapsulation efficiency the less product that is been lost resulting in lower financial costs.
INSTRUMENTS

Zetasizer ZS90
(Malvern Instruments)

Nanosight LM10
(Malvern Panalytical)
With the Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) technique the concentration of particles (particles/ml) can be determined.
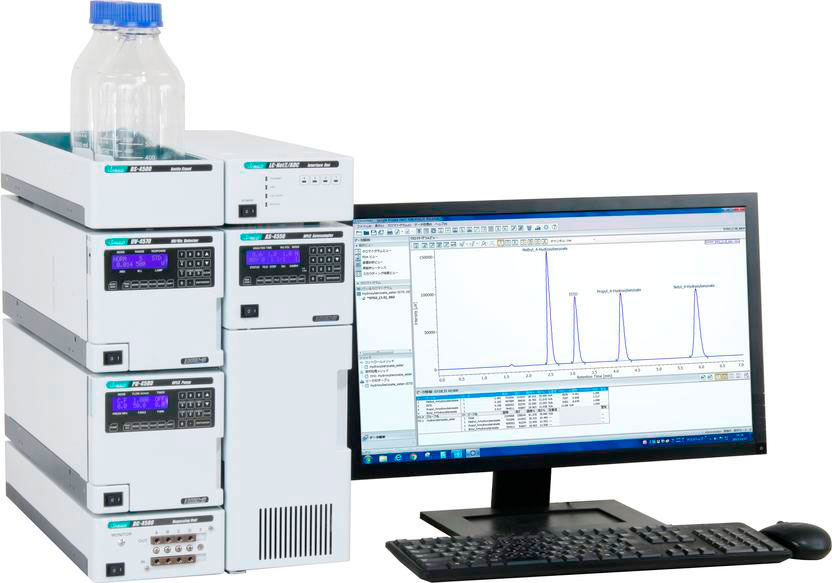

UHPLC/HPLC DETECTOR UV-VIS
(Shimazdu)

Synergy HTX Multimode Microplate Reader
(Biotek)
Other instruments we have access to:
Transmission Electron
Microscope
(TEM)
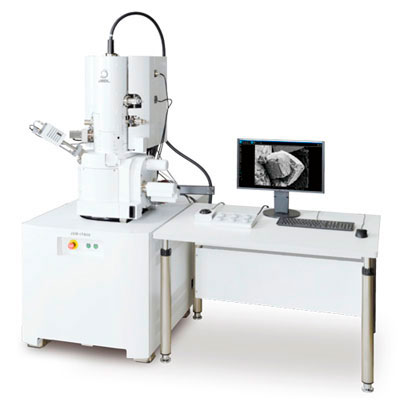

Scanning Electron
Microscope
(SEM)
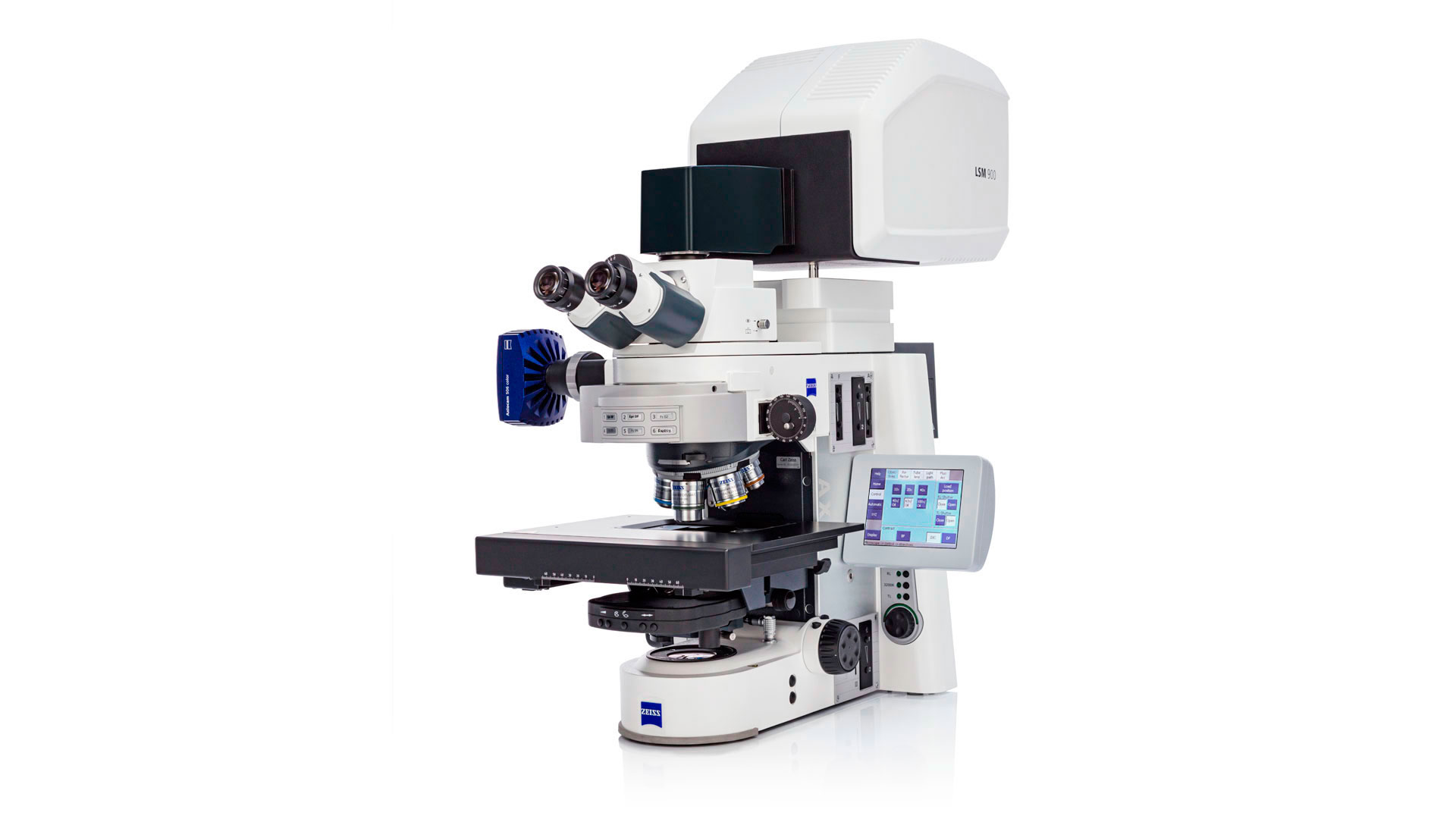

Laer Scanning
Confocal Microscope
(LSCM)
